2.1 Absolute / incremental dimensioning: G90/G91, AC/IC
1. G90:Absolute dimensioning
2. G91:Incremental dimensioning
3. Z=AC(…):Absolute dimensioning for a certain axis (here: Z axis), non−modal
4. Z=IC(…):Incremental dimensioning for a certain axis (here: Z axis), non−modal
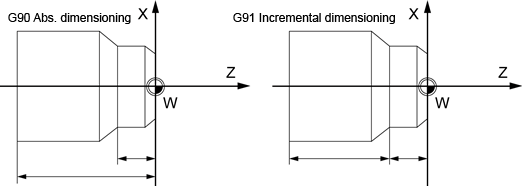
Fig.2.1 Different dimensioning types in the drawing
Explanation:
1. With absolute dimensioning, the dimensioning data refers to the zero point of the currently active coordinate system (workpiece or current workpiece coordinate system or machine coordinate system). This is dependent on which offsets are currently active: programmable, settable, or no offsets. With incremental dimensioning, the numerical value of the path information corresponds to the axis path to be traversed.
2. After the end point coordinate, write an equality sign. The value must be specified in parentheses (round brackets). Absolute dimensions are also possible for circle center points using =AC(...). Otherwise, thereference point for the circle center is the circle starting point.
3. G90 and G91 are modally active, Upon program start, G90 is active for all axes and remains active until it is deselected in a subsequent block by G91. Ac and IC are non-modal instruction.